|
|
 |
 |
|
Click on the Parashah name to read the summary:
|
 |
 |
|
Wed. April 30th - Thurs. May 1st
|
 |
 |
|
Israel's Independence Day....
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
The date for Yom Ha'atzmaut can vary from year to year. For instance, it may be moved a day earlier (i.e., to Iyyar 4th) so that it will not conflict with the weekly Sabbath. On our secular calendar this year Independence Day is observed Wednesday, April 30th at sundown until the following sundown on Thursday, May 5th.
|
|
 |
 |
|
Note that the word atzma'i (עַצְמָאִי) means "independent" in Hebrew. The word atzma'ut (עַצְמָאוּת) means the state of independence, which comes from atzmi - "my bones" (עֶצֶם). Hence the "Day of Independence" is called Yom Ha'atzmaut in Hebrew. The name reminds us of God's promise to revive the "dry bones" (עֲצָמוֹת) of Israel by bringing the Jewish people back from their long exile (see Ezek. 37:4-5).
עַם יִשְׂרָאֵל חַי / am Yisrael chai: "The people of Israel live!" The nation of Israel is God's "super sign" that He is faithful to His covenant promises (Jer. 31:35-37). Celebrating Israel's independence acknowledges God's loyal love for us all.
|
 |
 |
|
Theodor Herzl Day - May 8th
|
 |
 |
|
Herzl Day (i.e., Yom Herztl: יום הרצל) was established by the Israeli Knesset to commemorate the achievements and Zionist vision of Theodor Herzl (1860-1904), considered by many to be the father of the modern State of Israel. Herzl Day is observed on Theodor Herzl's birthday (Iyyar 10th) unless that day happens to fall on a Sabbath, in which case it will be postponed until the following day.
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
Herzl Day is commemorated by a state memorial service held on Mount Herzl in Jerusalem, the site of Israel's national cemetery. As the father of modern Zionism, Herzl's tomb is located at the top of the hill. His memorial faces the Mount of Olives from a distance. In addition to the burial site of Theodor Herzl, many great leaders of the Modern State of Israel are buried there as well. For this reason Mount Herzl is the venue for many commemorative events and national celebrations.
This year Herzl Day will be observed Thursday, May 8th.
|
 |
 |
 |
|
This week's Torah:
|
|
|
|
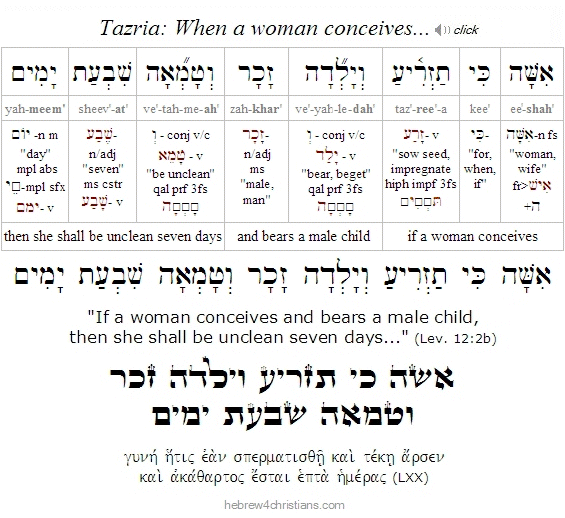
Tazria - Laws of Purity and Impurity
|
 |
 |
|
Because this is not a leap year, this week we have a "double portion" of Torah readings, both parashat Tazria (Lev. 12:1-13:59) as well as parashat Metzora (Lev. 14:1-15:33).
Our first reading, Tazria, continues the discussion of the laws of "purity" and "impurity" that began earlier with parashat Tzav. A new mother is regarded as a niddah (a menstruent woman) and is considered "impure" (tamei) regarding the sanctuary for 40 days (if a boy) or 80 days (if a girl). On the eighth day of life a boy must be circumcised. After the mother's "period of impurity" had ended, she was required to bring a yearling sheep as a burnt offering and a dove for a sin offering (if she is poor, two doves sufficed for both offerings).
The portion goes on to describe certain afflictions, collectively called tzara'at, that cause the affected person (or thing) to be both ritually impure (tamei) and in a state of uncleanness (i.e., tumah: טומאה). Note that tzara'at is not to be identified with "leprosy" (as some English translations claim), since the symptoms of tzara'at included not just the afflicted person's skin, but sometimes his clothes, pottery vessels, and house.
When applied to people, tzara'at indicates a sort of a spiritual affliction (i.e., yisur: יסור) that could only be diagnosed by a kohen (priest), not a doctor. If white or pink patches appeared on a person's skin, the afflicted person was required to contact a kohen for an examination. If the priest detected 1) two hairs that had turned white within the spot, or 2) a piece of healthy skin in the middle of the spot, he was declared tamei (unclean), and then had to follow the prescribed laws for the metzora (person affected with tzara'at); otherwise he was declared tahor (clean).
On the other hand, if the priest suspected tzara'at but was unsure, the afflicted person was quarantined and required to perform teshuvah (repentance). If a second evaluation indicated that the spot(s) had grown larger in size, the person was declared tamei and was subject to the laws for the metzora (i.e., dwelling "outside the camp" until the person was completely healed).
If someone was diagnosed with tzara'at, they were forced to leave the community and live in a state of exile. He had to tear his clothes like a mourner, put a shroud over his face (descending to his upper lip) and remain alone. If anyone came near, the metzora was required to cry out: "Unclean! Stay away! Do not become impure because of me!" (no one was permitted to come within eight feet of him). While so isolated, the person would have opportunity to perform teshuvah and seek spiritual "rebirth" (as described in the following Torah portion, parashat Metzora).
|
 |
 |
 |
|
The Second Torah Reading:
|
|
|
|
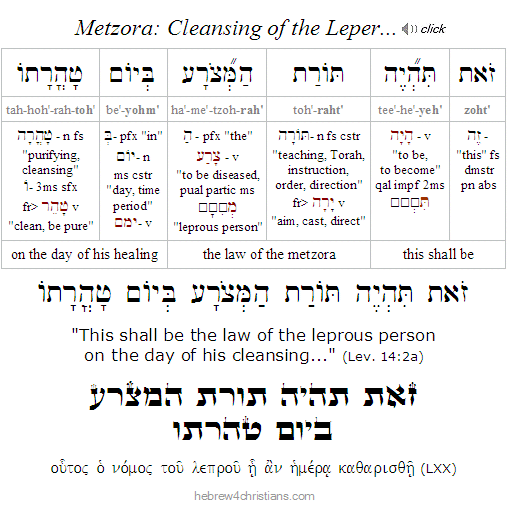
Metzora: Cleansing of the Leper...
|
 |
 |
|
As noted above, parashat Tazria explained that if someone was diagnosed with tzara'at ("leprosy"), they were forced to leave the community and live in a state of exile. The afflicted person (called a metzora) tore his clothes like a mourner, put a shroud over his face, and remained alone. If anyone came near, the person would cry out: "Unclean! Stay away! Do not become impure because of me!" While so isolated, the person would have opportunity to perform teshuvah (repentance) and to reexamine his relationship with God.
In our second portion this week (Metzora), we learn about the laws for cleansing "lepers." If the one suffering from tzara'at (i.e., the metzora) had apparently been healed, he would first call for the priest to be officially reexamined. If the priest saw no sign of tumah (uncleanness), a second examination was scheduled seven days later, and if the metzora was free from any sign of the disease, the process of tahara (purification) would begin.
The purification process was somewhat elaborate: After the second examination, the priest required that the metzora bring the following items for his cleansing:
- An earthenware bowl filled with spring water (mayim chayim)
- Two birds of the same type (whether turtledoves or pigeons)
- A stick of cedar wood
- A hyssop branch
- A scarlet thread
The priest then commanded that one of the birds should be slaughtered over the earthen vessel filled with fresh water, with its blood mixing with the water. The living bird, the piece of cedar, and the hyssop branch were then tied together using the scarlet thread, and the entire bundle was dipped into the earthen vessel. The blood and water mixture was then sprinkled seven times on the healed metzora, and the living bird was then set free.
Next, the afflicted person washed his clothes, shaved off all his hair (including his eyebrows), and bathed in a mikveh (ritual pool for cleansing). After that he could return to the camp - but he could not return to his home for another seven days. On the eighth day he would bathe again and offer several offerings (a chatat, an asham, an olah, and a minchah), but the blood from the asham (guilt) offering was mixed with oil and applied to his earlobe, thumb and foot, similar to the blood applied to the priests during their ordination. Oil from a meal offering was sprinkled seven times in the direction of the Sanctuary. Only after all this was he pronounced tahor (clean) by the priest. His life of uncleanness would be over, and he would be like a man who was brought back from the dead to new life.
This purification ritual corresponded with other rituals revealed in the Torah. The sprinkling of the hyssop by the priest recalled both the blood of the Passover lamb and the sprinkling of the ashes of the Red Heifer that cleanse from contact with death; the offering made of the two birds - one which was sacrificed and the other set free - recalled the scapegoat of the Yom Kippur ritual. The washing of garments, the shaving of all hair, and the immersion in a mikveh recalled the birth of the Jewish people at the Sea of Reeds. The blood of the guilt offering applied to the earlobe, thumb and foot, recalled the dedication of Aaron and his sons as the priests of Israel (Lev. 14:14). In other words, the individual purification process mirrored the purification of the community of Israel, and healing ultimately meant being reidentified as a redeemed child of God. In a very literal sense, then, we see how the metzora was "reborn" by water and by the blood (John 3:5; 19:34; Heb. 9:19).
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Countdown to Shavuout (Pentecost)
|
|
|
|
In the Torah we are instructed to count forty nine days – seven weeks of days – from the day following Passover until the jubilee holiday of Shavuot (i.e., Weeks or "Pentecost"). This period of time is called Sefirat HaOmer (ספירות העומר), or the "counting the [barley] sheaves" (see Lev. 23:15-16; Deut. 16:9). In abstract terms, it's as if there is a dotted line pointing directly from Passover to Shavuot - a "Jubilee" of days - representing the climax of Passover itself:
![Spring Holiday Timeline (H4C]](../../Scripture/Parashah/pesachline.gif) |
The early sages identified this jubillee that marks the seventh week of weeks to commemorated he revelation of the Torah at Sinai (which did happen exactly 49 days after the Passover in Egypt), however the New Testament identifies it with the outpouring of the Holy Spirit (רוח הקודש) that ratified the reality of the New Covenant of God at Zion. The redemption process that began at Passover was therefore completed at Shavuot, and that "completion" was the revelation of God's love and deliverance for the entire world.
Moreover, although the Jewish sages did not fathom the use of the otherwise forbidden leaven in the offering (see Eph. 2:14). The countdown to Shavuot therefore goes beyond the giving of Torah at Sinai and points to the greater revelation of Zion. Shavuot is the fulfillment of the promise of the Holy Spirit's advent to those who are trusting in Messiah (Acts 2:1-4). "Counting the Omer," then, is about receiving the Holy Spirit to experience and know the resurrected LORD of Glory. You can "count" on that, chaverim!
In this connection it is important to understand that the climax of the 49 days was not the giving of the law at Sinai (i.e., matan Torah), but rather the revelation of the altar (i.e., the"Tabernacle") and its subsequent fulfillment in the sacrificial death of Yeshua as our Lamb of God. Moreover, it was during this time that Yeshua made His post-resurrection appearances to His disciples and indeed ascended to heaven during this period...
Of particular importance during this count down time are the following: 1) the beginning of the count of the omer since it signified the waving of the firstfruits and therefore the resurrection of Yeshua (1 Cor. 15:20); 2) the 40th day of the Omer (Mem B'Omer), when Yeshua ascended back to heaven, and 3) the climactic 49th day of the Omer (Shavuot) when the Holy Spirit was given to the disciples in fulfillment of the promise that we would not be left comfortless (Acts 2:1-4). It should be clear, then, that Shavuot marks the time of "Jubilee" of the Spirit, when we are clothed with power to serve the LORD without fear...
 |
Hebrew Lesson
Deuteronomy 16:9-10 reading:
"Pentecost Sunday?"
Most Christian traditions teach that Shavuot (i.e., "Pentecost") must fall on a Sunday, the "day after the Sabbath," which therefore must be the seventh Sunday after the Saturday of Passover Week, but the traditional Jewish sages did not interpret the "day after the Sabbath" (מִמָּחֳרַת הַשַּׁבָּת) to refer to the weekly Sabbath, that is, to Saturday, but rather to the Sabbath of the Passover, which is the context of the commandment given in the Torah (Lev. 23:15). In other words, if we interpret "the day after the Sabbath" to refer to the Sabbath of the Passover, then the 49 day count would begin on Nisan 16, regardless of the day of the week that falls on the calendar, and therefore Pentecost would fall 49 days later, on Sivan 6, again, regardless of the day of the week that happens to fall on the calendar.
|
|
|
Blessing before Torah Study:
|
|
|
|
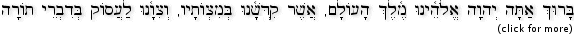 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Some terms:
|
|
|
|
- Parashah is the weekly Scripture portion taken from the Torah. Each parashah is given a name and is usually referred to as "parashat - name" (e.g., parashat Noach). For more information about weekly readings, click here.
- Aliyot refer to a smaller sections of the weekly parashah that are assigned to people of the congregation for public reading during the Torah Reading service. In most congregations it is customary for the person "called up" to recite a blessing for the Torah before and after the assigned section is recited by the cantor. For Shabbat services, there are seven aliyot (and a concluding portion called a maftir). The person who is called to make aliyah is referred to as an oleh (olah, if female).
- Maftir refers to the last Torah aliyah of the Torah chanting service (normally a brief repetition of the 7th aliyah, though on holidays the Maftir portion usually focuses on the Holiday as described in the Torah). The person who recites the Maftir blessing also recites the blessing over the Haftarah portion.
- Haftarah refers to an additional portion from the Nevi'im (Prophets) read after the weekly Torah portion. The person who made the maftir blessing also recites the blessing for the Haftarah, and may even read the Haftarah before the congregation.
- Brit Chadashah refers to New Testament readings which are added to the traditional Torah Reading cycle. Often blessings over the Brit Chadashah are recited before and after the readings.
- Mei Ketuvim refers to a portion read from the Ketuvim, or writings in the Tanakh. Readings from the Ketuvim are usually reserved for Jewish holidays at the synagogue.
- Perek Yomi Tehillim refers to the daily portion of psalms (mizmorim) recited so that the entire book of Psalms (Tehillim) is read through in a month. For a schedule, of daily Psalm readings, click here.
- Gelilah refers to the tying up and covering the Sefer Torah (Torah Scroll) as an honor in the synagogue.
- Divrei Torah ("words of Torah") refers to a commentary, a sermon, or devotional on the Torah portion of the week.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Related Topics:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<< Return
|
|
|
|
Hebrew for Christians
Copyright © John J. Parsons
All rights reserved.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|








![Spring Holiday Timeline (H4C]](../../Scripture/Parashah/pesachline.gif)

